Types of electric cars
We’ve seen so much technological development nowadays in different aspects of our daily lives, and the automotive industry is no different. With the call for boosting fuel efficiency, lowering fuel consumption, and manufacturing cars that are more environmentally friendly, most automakers are now also taking the advantage of having an alternative fuel which is electricity to create electrified cars
Electric powered cars trace its past from the 1880s. Although most of the models produced were not for commercial distribution, this was once of the best technological innovation that has been done for the transportation industry.
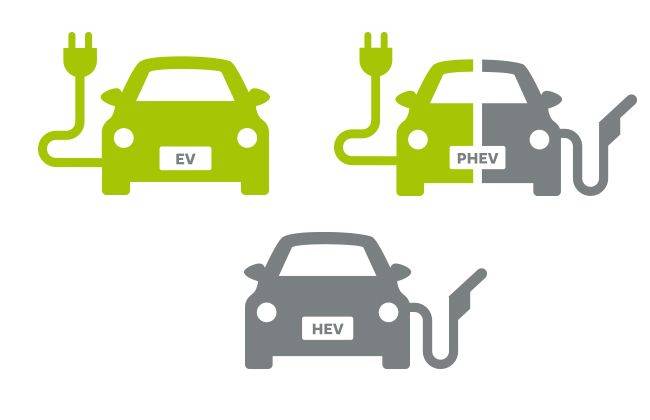
Electric vehicles or cars, also known as EVs, are types of vehicles that are driven by one or more electric motors using energy stored in rechargeable batteries instead of an internal combustion engine alone.

Aside from being environment-friendly, reducing or completely eliminating your fuel cost, electric vehicles are also very responsive and have a very good turning effect since the electric motor reacts quickly. On the other hand, electricity prices or fees are much more stable than fuel and maintenance costs and general running costs are also more affordable with an EV too.
Also Read: EV vs Regular Combustion Engine
There are several well-known types of electric vehicles that are out in the market based on their powertrain configuration. Let’s take a look at their specs:
MILD HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE
If you haven’t had experience with an electric vehicle before, a mild hybrid electric vehicle can easily introduce you to its benefits and smooth driving experience compared to a full hybrid vehicle. It combines the best of both worlds, which are petrol and electricity, and typically is the most affordable way to hybrid ownership.
The mild-hybrid kinds of vehicles are powered by more than one energy source for their propulsion - mainly by petrol in an internal combustion engine assisted by electricity in an electric motor to reduce the amount of work it needs to do. It has a stop/start system, a smaller battery, and a motor-generator that can both create electricity and help boost the gasoline engine. It also allows the engine to switch off at a lower speed setting or when you’re stationary, braking or cruising. These make for lower fuel consumption yet still reducing emissions. Nonetheless, it doesn’t attain the same level of fuel efficiency improvement as compared to full hybrid models.
The battery can be charged by regenerative braking, because of this function, it is not necessary for it to be plugged into a power source. However, it also could not move using just electric power as all movements are generated by the internal combustion engine.
An example of the mild hybrid car would be the Honda Civic Hybrid, Chevrolet Silverado Hybrid, and 2020 Mercedes-Benz GLE.

STRONG HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Strong or full hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, are vehicles that can run on either only by the combustion engine, the electric motor or give you a strong boost of power with the combination of both. Unlike the mild hybrid, where the electric motor cannot power the car on its own, you can enjoy pure electric power for up to 50% in a full hybrid vehicle. Although the vehicle can also be powered by an internal combustion engine, this type of hybrid can also run completely on electricity over short distances.
By inter-converting mechanical and electrical power, it selects the best mix of internal combustion engine and electric resource in a split power path to give you more flexibility for your driving experience. Also, since the strong hybrids models can hold limited amounts of electric charge, it can be used to provide an added boost with the combustion engine, thus improving its fuel economy more.
Even though the power required in starting the vehicle is generated by the gasoline engine beforehand, the electric motor in a full hybrid will most likely be used the entire time that the vehicle is running and the battery can be charged even with the lack of the main supply.
The Toyota Prius and Ford Escape are both examples of strong or full hybrid vehicles.
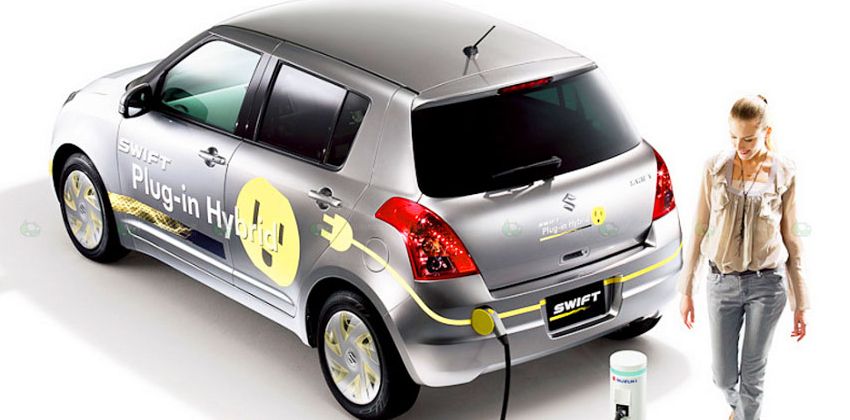

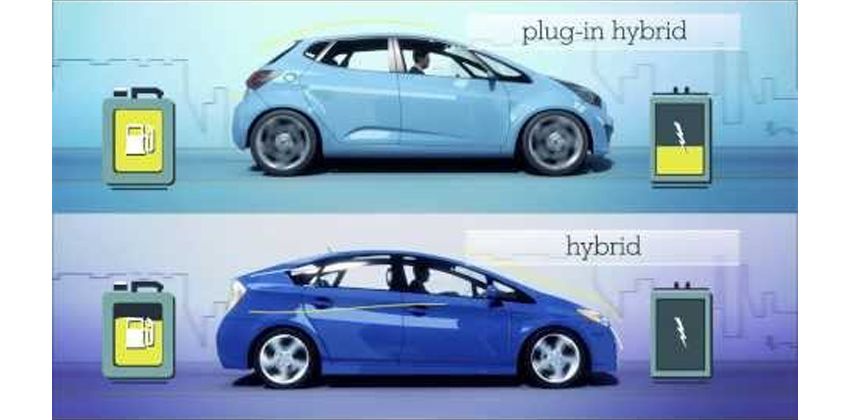
PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle or PHEV is an exceptional vehicle that is similar to electric hybrid vehicles but, as the name suggests, can be plugged in to charge its electric batteries. It is also said to be across from a hybrid vehicle and a fully electric one because of this function.
They can run without producing emission over longer distances unlike the first two hybrids and once the batteries charge became insufficient the engine automatically takes over. PHEVs also have higher capacity in terms of its battery compared to HEVs but can use regenerative braking to get it charged like the mild and strong hybrids.
It also has a lower total cost of ownership and lesser to zero carbon emissions based on usage.
If you charge this vehicle overnight and drive it to your daily short trips and commutes you can use the car with all of the electric motor function and reduce or eliminate your fuel consumption completely.
Don’t have time to charge? No worries as it still can function as a conventional hybrid while using the gasoline engine once the electricity resource is depleted. Hence, charging the battery won’t be mandatory.
You might want to check Toyota Prius PHV and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV for these kinds of vehicles.
Also Read: 7 Smart tips to extend your EVs battery life
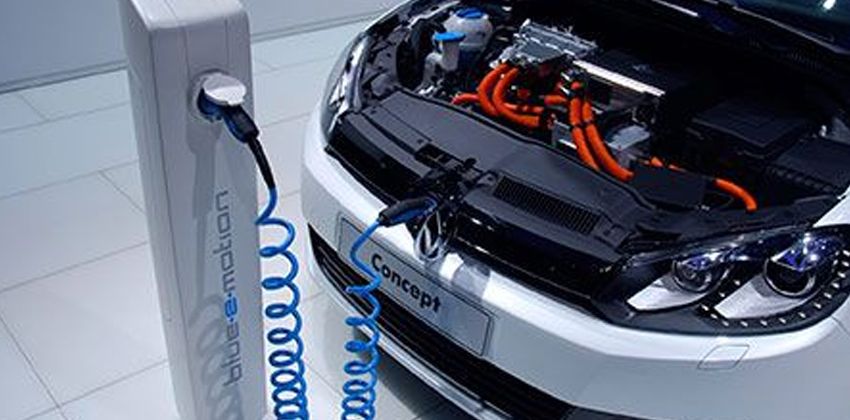

BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE
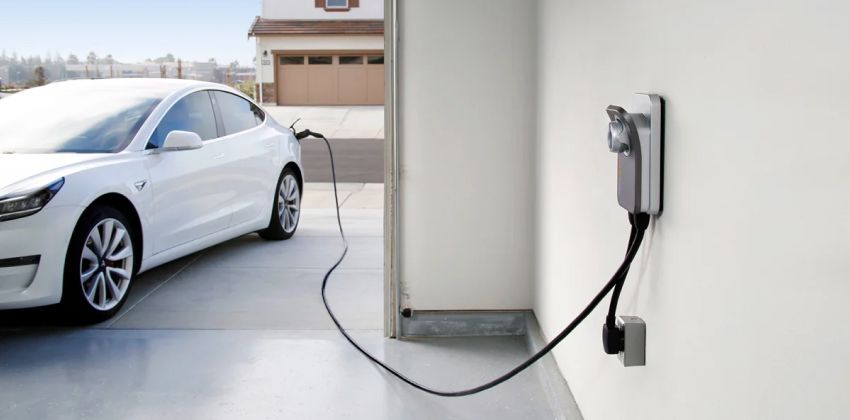
Also known as the BEVs, the battery-electric vehicles are the fully-electric vehicles with rechargeable batteries and no gasoline engine. Instead of a fuel tank, this vehicle stores electricity onboard through high-capacity battery packs. The main good thing about BEVs is that it doesn’t produce any harmful emissions that are hazardous to both humans and the environment. BEVs are charged by electricity from an external source and its chargers are classified into three based on their respective speed to fully recharge:
Level 1 Charging - To charge this vehicle, it will use a standard household outlet with 120v and takes around 8 hours to be fully charged. This amount of power can cover approximately 75-80 miles already and it is one of the most common chargers that have the capability to be utilized onto most EVs in the market.
Level 2 Charging - This kind of charging usually utilizes a specialized station that provides an outlet with 240v. In order to cover up a distance of 75-80 miles, this charger needs at least 4 hours to finish. It can be typically found at workplaces and public charging stations.
Level 3 Charging or DC Fast Charging - Known also as ‘fast charging’, this is the current fastest charging solution for electric vehicles in the automotive industry. This type of charger is found ad dedicated EV charging stations and will only take 30 minutes to be fully charged and cover a distance of 90 miles.
Some examples of this car are the Tesla Model 3, BMW ii3, Chevy Volt, Chevy Spark, Nissan LEAF, and Ford Focus Electric.
Our two cents worth: With the fast-paced progress in terms of automotive technology, it would not be surprising to see more automakers creating their own versions of electric cars or even motorcycles, which is also available for quite some time already.
After all, it is not just about the trend or the need to do so but more like an innovative answer to the existing problems faced by our environment because of the gas emissions by gasoline or diesel-powered engines. Although this is not the sole solution to everything, this is already a big step towards a holistic approach to solving global warming without compromising the continuously growing automotive industry.
For more amazing stories about everything that’s about cars and motorcycles, stay tuned to our articles here at Zigwheels Philippines!
Also Read: 7 Common electric car myths busted
Sell your car at the best price
 Verified and genuine buyers
Verified and genuine buyers
PIMS 2024
Trending & Fresh Updates
- Latest
- Popular
You might also be interested in
- News
- Featured Stories
Featured Cars
- Latest
- Upcoming
- Popular
Latest Car Videos on Zigwheels

Car Articles From Carmudi
- journal
- advice
- financing
- insurance











































































